Joel Hunter is an ordained minister and has a doctorate in Culture and Personality in Pastoral Care. He is presently senior pastor at Northland Church, in Longwood, Florida and in 2009-2010 sat on Obama’s Office of Faith-based and Neighborhood Partnerships.
Joel Hunter is an ordained minister and has a doctorate in Culture and Personality in Pastoral Care. He is presently senior pastor at Northland Church, in Longwood, Florida and in 2009-2010 sat on Obama’s Office of Faith-based and Neighborhood Partnerships.
Northland is “a church distributed,” meeting in several locations in mid-Florida to serve a widely dispersed community. This requires several pastors to work together, among them the soft-spoken Amer-Indian Vernon Rainwater, who after time in the military, got a degree in social work, then was ordained, and came to Northland in 1990.
The church was originally built in an old roller-skating rink. The growth of the congregation has allowed it to build a larger building next door, with airy hallways, offices, classrooms, conference rooms, café, book store, and sanctuary that seats 3,100 ... in addition to the thousands who attend online. Several screens throughout the church project the pastor as he preaches and they scroll the words to the songs that have replaced more traditional Protestant hymns—which creates something of a church karaoke. A twelve-voice choir and eight-piece band accompany. Additional services are offered on Saturday night and Monday evening, with about one thousand attending each.
The Sunday after Sept. 11th, Northland held a joint online service with a church in Egypt as a protest against polarization between Americans and Arabs. The church also provided volunteers to protect Muslim women from anti-Muslim attacks as they went around town.
In 2009, Becky Hunter, Senior Pastor Joel Hunter’s wife, stepped down from the presidency of Global Pastors’ Wives Network, where, “We get everything, from training women as public speakers to Muslim women who converted to Christianity and need to know what they should study--quickly.” About Northland she says, “No one is obliged to have any particular confession to pray or become a member at Northland--no denominational version--but agreement to historic creeds of the church are required. But if you do join, you are committing to have a ministry aspect, a service aspect, in your life. There’s no ‘pew gum’ here.”
Northland has ministries in: marriage counseling, divorce, grieving, substance abuse, cancer, applying Scriptural values to business, orphans, foster children, the homeless, free food and clothing distribution, the elderly, the deaf, and “people struggling with homosexuality.” Its prison ministry ranges from running prayer services to helping prisoners develop plans for their lives after release. The church has an employment network, several men’s groups, groups for both men and women post-abortion “without judgment,” and discussion groups on faith and science. One Heart, a Northland partner, works with city and county agencies to repair the homes of the area’s poor. The church also has a bowling club, soccer games, a motorcycle group, and classes for children, including a course in Mandarin.
Overseas, the church works with national and international organizations in Egypt, South Africa, Brazil, Sri Lanka, Argentina, China and the Ukraine. For Catholic or Orthodox Ukranians, the appeal of evangelicalism stems, according to Northland co-pastor, Dan Lacich, from evangelical hope and optimism. “The Ukrainians I’ve met view the Orthodox church as defeatist; it just hung on during the Soviet years—‘we’re going to circle the wagons’ rather than ‘we’re going to make a difference.’”
In South Africa, Northland partners with the Vredlust Dutch Reformed church to build a school and do community development in a small town in Swaziland. The project is run, as Lacich put it, “by people who instead of taking a vacation at the beach volunteer for Swaziland. What started out as two camp fires and a kettle is now several classroom buildings, a medical clinic, and we’re doing micro-loans for business start ups.” The funding comes in large part from a young Vredlust couple who earmarked what they needed each year to live and donate everything else they earn to a trust for ministry. Northland contributed an additional thirty to forty thousand dollars in 2009, and overall spends roughly $1.5 million a year on social justice projects, about 20 percent of church income.
“We do not tell a community,” Vernon Rainwater notes, “that we know what their problems are and how to fix them. We try to find out what the perspective of the community is, and we often learn more than they do.” Compassion International, another Northland partner, began in 1952 to bring food, clothing and education to children orphaned in the Korean War; today it serves children throughout the developing world. Another partner, With This Ring, uses funds from the sale of jewelry (and other products) to dig clean wells in Africa. It estimates that it cost “one hundred and eighty thousand dollars to save the lives of thirty thousand people in Yendi. That’s six dollars a life—the cost of a latte and a cookie.”
Hunter recalls that he was the kind of kid whose formative religious experiences included getting caught stealing a “men’s magazine” and whose first church skill was coughing loudly enough to cover the sound of opening candy wrappers. At Ohio University, he became active in the Civil Rights movement.
JH: [I] assumed, as we all did, that if we just got the right power in office, we’d be alright. When Dr. King was assassinated, I was thrown into a crisis. The volatility and polarization of that time—we didn’t have graduation ceremonies because we had eight hundred National Guardsmen on campus—could get you caught up in politics without your knowing why you were doing it. I wanted a more stable foundation for political reform, an eternal reason, a deep kind of equality where all God’s children would be cared for because He cared for them. So I committed myself personally to follow Christ as a result of that search for foundational meaning.. I thought I’d go to seminary—though I was sure they’d throw me out as soon as they found out about me. I wasn’t exactly the religious type.”
JH: Dr. King is partially why I identify with Barack Obama. King integrated faith with social policy in a way that benefits the vulnerable—which is our job. That’s Jesus’ reading of his job description in Isaiah 61. My grandparents were always broke because they were always giving their money away. On the other hand, I lived in an all-white town. So my journey was religious and social; it was part of my faith to learn to understand the common good.
In the next ten years we’re going to see more cooperation between those who form public policy from a secular perspective and those who come to it from a religious one. This is part of the maturation of the evangelical movement and in a way a going back to our roots. Christianity started out as a compassionate movement. It grew because we responded to epidemics and catastrophes. We were for abolition, women’s suffrage, and child labor laws. In maturity, you define yourself by what you’re for, by how you can cooperate with those who aren’t like you. There’s an emerging constituency that, while not leaving behind earlier concerns, is putting a major amount of energy into climate change, poverty, justice issues, health issues. You’re seeing a new evangelical maturity.
The iteration of the 1970s was a political, alarmed reaction to the perceived decadence in our culture, like abortion and the extraction of prayer from the public schools. For a couple of decades, the evangelical movement got stuck in this combative—“we have to win”—stance. There were issues where I agreed with [religious right leader Jerry] Falwell, like being pro-life, but the tone was off-putting. There was a silent majority to the silent majority. There came a time when many people started cringing. The AIDS issue—shouldn’t these people be receiving the most compassion and understanding? There are twenty-five thousand children dying every day from poverty. What are we doing about that?
MP: Is this a generational change?
JH: Younger people are less ideological, care less about Democrat and Republican. They just want to get things done. But there’s a lot now that reminds me of the 1960s—inspirational, idealistic. I have lived a long time to see this come about again.
MP: Is it a response to the Bush years?
JH: Let’s say the Bush-Cheney years. Bush went in a compassionate conservative—at least that’s who some of us voted for. But I’m not sure he had the capacity to handle the issues. So he delegated to Cheney.
There is a sense now among evangelicals that we did not think independently; we did not examine or analyze. We went along with this self-protective mentality that says, ‘let’s get them before they get us.’ September eleventh [2001] reinforced this but there already was a good deal of fodder to shape into fear. We’ve developed a consumerist, self-centered culture. That feeds into pre-emptive war because we fear that ‘they’re going to take away what I have.’ Or ‘Government programs are going to take away my hard-earned dollars.’ There are remnants of that now, in right-wing talk radio-- Limbaugh, Hannity, Michael Savage—just awful.
Here’s what I think the enemy is: the luxury of being simplistic, of not understanding how complex problems are and how much cooperation is required to solve them. Evangelicals went through a period where we formed homogeneous affinity groups. You cloister together and think everybody else is the enemy. One reason I’m thrilled with Obama’s presidency is that he likes a broad spectrum of perspectives. Out of those he will glean a practical solution good for everyone. He’s got the intellectual capacity to handle the job.
MP: Is your congregation bi-partisan?
JH: We’re nearly half and half.
MP: If you want to contribute to society but not marry a political party, how does that work?
JH: If you’re a Christian and want to make a difference in the world you ask: what is the Biblical basis for what I do? What would Jesus do? We can’t bank on winning or losing political battles. That’s not what the kingdom of God depends on.
We, being the humans we are, will always be tempted to make spiritual progress by political means--to use power in order to make others have our values. But Christians have to be careful to exemplify what we believe is right and then let it go. There three hundred million people in this country. I am one voice.
What I saw on the religious right was a lot of religious arrogance. Those who are theocrats—the Reconstructionists who insist that Biblical mandates be law for everybody-- will always believe they’re losing if they don’t get their way. We believe we are winning if we have the freedom to give our opinion along with everybody else. We don’t need to have our way. God doesn’t call us to be “successful”; he calls us to be faithful.
MP: If you are one voice, how do you work with other voices?
JH: We have extensive partnerships in our work on poverty, medical clinics, AIDS, housing. We partner with governments all over the world. Locally, when we have convocations on torture, creation care, and poverty, I ask for broad leadership: the bishop of the Catholic church, the head of the Islamic Society, a rabbi. I ask them to explain, from the perspective of their Scriptures, why this issue is important. Everybody begins to understand that “they” have values like I do and that this issue is too big for any one group to solve.
I was on the board of Jobs Partnership of Central Florida. The state government offered the finances to train the unemployed, and individual church-people became volunteer sponsors for each unemployed person. The sponsors said, “If your kid gets sick, we’ll take him or her to the doctor. If your car breaks down, we’ll get you to work and fix the flat problem.” Since the business community was getting trained employees with backup support systems, they committed to taking the trainees into jobs where they could move into higher-paying ranks. Business people got what they needed. Church people were able to love like they needed to love. Government got people off of welfare into jobs.
Of course, there are still a lot of barriers to working together—not willful ones but we’ve gotten used to operating on our own realms. Having said that, we specifically invite the African American church, other churches and faith communities into much of what that we do. We have a few that are our long-time partners. Same is true for our missions in other countries. We want to form partnerships—long term partnerships with people who are different from they way we are. Westerners have a view of the Gospel that’s very different from someone in South America, China or Africa. We need that kind of cross-pollination.
MP: In cooperative projects, how do you handle the finances?
JH: A church cannot take government funds into the church’s general budget. So for instance, in our partnership with the county to renovate houses in poor areas, they buy the supplies and the churches bring in the [volunteer] craftsmen. The county pays for the materials; the money never comes to us.
MP: What could mess up this picture of inter-group and church-state cooperation?
JH: Militancy from one powerful group. If any group gets too much power, there is a tendency to suppress others. But as we continue listening with respect to multiple perspectives, we will begin to trust each other. I’ve been in conversations with organizations our government can’t even talk to—like Hezbollah. The enemy is never as scary or threatening up close.
What also can sabotage dialogue is a structure where voices present their case to the governing authority but never have to listen to others. If you have a president who says, “give me one group at a time,” the group comes in, presents its case, and if things don’t go down their way, they’re furious. But if all the groups sit together and hear what other people are saying, then they begin to see where others are coming from.
MP: How do you answer those who think churches don’t belong in political discussion?
JH: We could diffuse some of the alarm if we think in terms of cooperation rather than “religion against secularism.” Think more in terms of cooperation on projects rather than compromise on beliefs. We need to get away from the zero-sum game that says, if we allow them their voice, it will take away from what I have.
MP: What’s your response to those who say, “We don’t want to dialogue with certain religious groups, like those that commit honor killings.”
JH: You take care of destructive behavior by law. All law is codified values, of course. But every society must decide what protecting its citizens entails. Yet you don’t disenfranchise an entire faith group because of some of the people in it. You know the saying, you keep your friends close and your enemies closer.
The counter-intuitive wisdom here is that the very people you don’t want to talk to are the people you need to talk to the most. You start out by saying that this is going to be tough. But you never make any progress until you engage in those conversations. At least you’re building relationships and that enhances the probability of reaching consensus.
There’s a very important conversation to be had with secular authorities about Muslims not being able to wear certain types of dress or Christians not being able to wear a cross of a certain size. Dialogue is necessary no matter how tough it is. Boundaries are not just dividing points. They are connecting points. They are not where the conversation ends but where it begins.
Used with permission.
By Marcia Pally
Copyright 2011, Eerdmans Publishing
http://www.amazon.com/New-Evangelicals-Expanding-Vision-Common/dp/0802866409
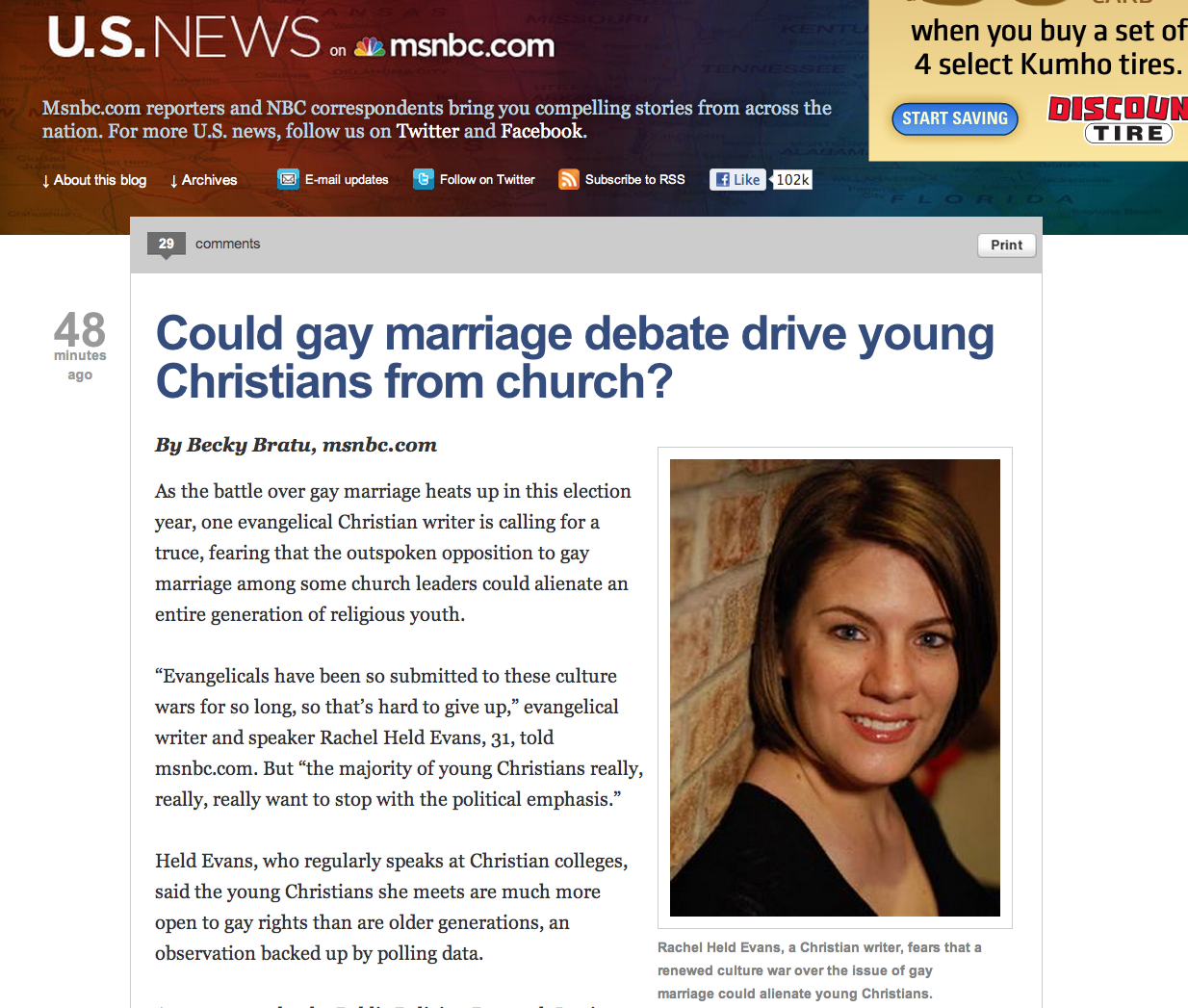 As the battle over gay marriage heats up in this election year, one evangelical Christian writer is calling for a truce, fearing that the outspoken opposition to gay marriage among some church leaders could alienate an entire generation of religious youth.
As the battle over gay marriage heats up in this election year, one evangelical Christian writer is calling for a truce, fearing that the outspoken opposition to gay marriage among some church leaders could alienate an entire generation of religious youth.